Table of Contents
AI is one of the biggest breakthroughs of this century. It has become such a prominent part of our lives that we sometimes don’t even notice it. Artificial intelligence has introduced multiple improvements to both customers and businesses, from personalised experiences to predictive analytics.
A lot of companies are already exploring the opportunities AI creates while reaping the benefits. Why doesn’t everybody do it?
The answer is simple — not every business needs AI or can benefit from it. Artificial intelligence is not a “magic wand” that can solve any problem; it still has limitations.
To determine whether your business will benefit from AI, we need to understand its impact and how to implement it.
See also: The rise of AI-native technologies
Why businesses are embracing AI: a detailed look
Think of any industry off the top of your head, and there’s probably an AI-powered solution for it. Artificial intelligence is literally everywhere — from small restaurants to global corporations. While some use it only on the client side to provide users personalised experiences, others opt for process automation or predictive analytics.
Every industry finds its own applications for AI.
For example, in retail, AI improves customer experience through chatbots, and item suggestions based on customer history. In the automotive industry, AI uses computer vision for damage detection and self-driving cars. There are countless examples, all leading to the same thought — AI is helpful. Recently, American computer scientist Andrew Ng pointed out the following.
In recent years, AI has become more accessible to small businesses, as Andrew puts it “democratisation of access to AI”, but does it influence the adoption rate? Take a look at the market.
Behind the hype: AI implementation market
According to Statista, the global AI market is expected to reach $244,200 million USD by the end of the year.
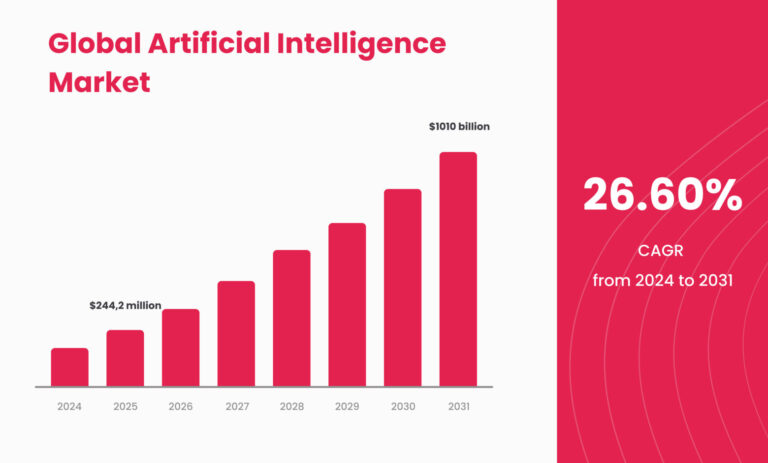
Businesses clearly see the potential benefits AI could bring, especially when combined with cloud computing and cloud storage solutions. Cloud technologies quite literally eliminate the most common challenges to AI adoption: the burden of maintenance and the need for extensive computing power. And since there are multiple open-source AI frameworks out there, adoption and customisation become even easier.
What AI adoption brings to the table
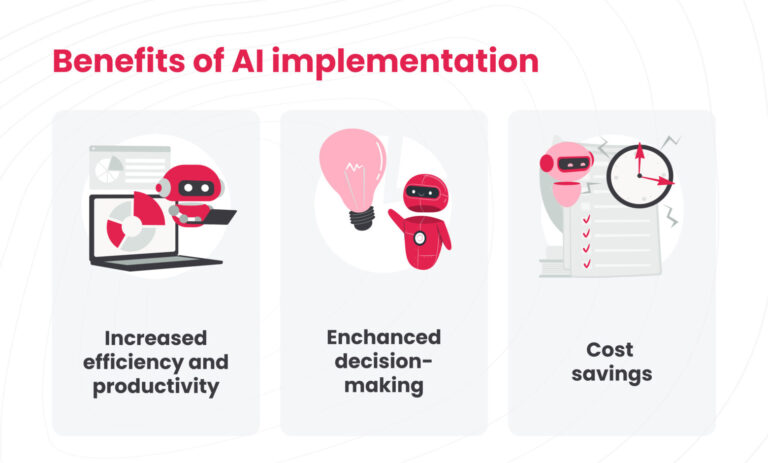
What are the “potential benefits” that businesses see in AI? Well, they highly depend on the type of AI and the industry, but the main benefits of implementing AI are the following.
Increased efficiency and productivity
The worst type of task is a tedious one: not challenging enough to be engaging, but complex to take up the entire day of your employee. Now, imagine this task done in a matter of minutes — or even seconds.
AI can automate the most tedious tasks, freeing up your employees’ time to focus on other objectives. And with time-consuming tasks out of the picture, employees’ productivity will rise, consequently increasing efficiency.
Enhanced decision-making
Every business processes an ocean of data, but not every business uses it. It’s clear; at some point, the amount of information becomes too big for humans to handle. That’s where AI comes in.
AI can analyse data, detect patterns, and provide suggestions based on trends it sees. Instead of relying on assumptions, businesses that use AI-powered analysis can make informed decisions that will lead to meaningful changes.
Cost savings
Despite the steep cost of implementing AI, it’s an investment that pays out over time. It’s not something you might notice in a short-term perspective, but it has a cumulative effect: the longer you use AI, the more ROI you’ll see.
AI implementation in business allows to stay ahead since it can predict market trends, identify new opportunities, and respond faster to changes. Those who leverage AI effectively can refine strategies, cut costs, and offer better services than their competitors.
See also: How generative AI is transforming EdTech
Does your business need AI? Key considerations before implementation
Natalie Semak, an Altamira Chief Delivery Officer, believes that: “Technology should solve problems, not create them. Sometimes the best innovations come from making complex things simple.”
Despite its benefits, not every business needs AI. Useful AI implementation happens if:
Business has too much data to process;
The workload consists of many tedious or repetitive tasks;
Company has difficulties scaling its operations;
Workflow heavily relies on forecasting and predicting trends.
While facing one (or all of the above) challenges, your business does need AI and it’s time to think about adopting it. However, proper AI implementation requires AI readiness. Phillipp Gerbert, the General Managing Director of Venture Labs, has told about AI implementation
How to implement AI in business: a step-by-step guide
AI implementation is no easy task and will vary in steps and difficulty depending on multiple factors. The industry, the software type, and the AI type are just a few of the many moving parts that could change. However, the rough outline of an AI implementation strategy is always the same.
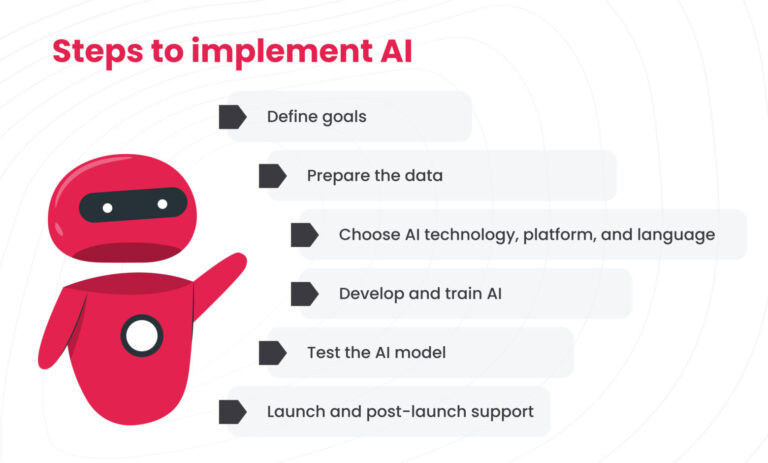
Step 1: Define goals
First off, you need a clear goal in mind. Consider which tasks you want AI to handle, and which ones still require human oversight. This will create an outline of what type of AI you’re looking for.
For example, you don’t need a computer vision for a simple chatbot, the same way it won’t be enough to use NLP-based AI for complex calculations.
As soon as the goals are decided, you’re ready for the next step.
Step 2: Prepare the data
To make AI bring the results, it needs training, which requires a lot of structured data, also known as training datasets. Make sure your data is clean, uncorrupted, and properly categorised since it will determine how good your AI model will be.
Step 3: Choose AI technology, platform, and language
With the variety of AI solutions out there, it’s hard not to feel overwhelmed. Finding the perfect fit for your goals is not an easy task either. Here’s what you need to look for:
AI model can handle tasks your business looking to solve;
Technical capabilities of your business are on par with AI operational requirements;
The setup, integration, and maintenance costs are in your budget range.
Usually, AI comes in three flavors: open-source, third-party developed, and custom-built AI. Each of the options has its own strong sides; for example, open-source is easy to customise but needs on-sight maintenance team. Third-party AI solves maintenance and update problems but doesn’t come cheap. Custom AI solutions account for all of the above but require in-house expertise.
AI platform
To develop, train, and deploy your AI, you will need a platform that provides you with the specific tools for this task. There are many platforms that offer the necessary tools for model development and training out there, but the most popular ones are:
Google platform, since it allows for multiple tools for AI development, such as AI Hub, AI Building Blocks, and AI Platform;
Microsoft Azure, which works perfectly for machine learning model deployment;
AWS Machine Learning, with an emphasis on providing companies with out-of-the-box analytics.
After deciding which platform to use, programming language is next.
Language
In most cases, AI development is done using one of these languages:
Python. It’s probably the most popular language for AI development due to its rich ecosystem of AI/ML libraries (e.g., TensorFlow, PyTorch, scikit-learn);
Java. Mostly used for enterprise AI software and big data processing, its scalability, stability, and strong multi-threading support, makes it suitable for AI systems that require high-performance concurrency;
C++. The most efficient option from the performance standpoint, mostly chosen for its speed, large number of frameworks, and integration with other languages.
Step 4: Develop and train AI
As soon as you decide on the platform and language, you can start developing AI model. Remember the training datasets you had to prepare earlier? They will serve as a “knowledge base” for your future AI.
There are different approaches to AI training:
A supervised approach is one where AI is trained using labelled data. In simple terms, AI is trained with labelled examples, allowing it to learn the relationship between input variables and the correct output. Once trained, the model can be applied to new, unseen data to make predictions or classifications;
An unsupervised approach, where AI uses unlabelled data from the start. This approach encourages the AI model to look for patterns and categorise data on its own;
A semi-supervised approach, which is a mix of both approaches above. It uses a small amount of labelled data as a reference point and a lot of unlabelled data.
Once the AI training is done, it’s time to test the results.
Step 5: Test the AI model
To ensure the AI model works as intended, it needs to be tested. There are multiple ways to do it:
Unit testing that uses predefined test cases to check every component;
Functional testing, which checks whether the AI model performs as intended;
Performance testing that monitors AI’s performance under high loads;
Security testing, that checks how secure AI is.
It’s best to use a combination of different tests for better coverage. On top of the methods of testing, there’s also a choice of how to test your data: quality assurance (QA) and automated quality assurance (AQA).
The only difference between QA and AQA is automation and speed of testing. AQA is faster but more expensive, while QA is cheaper but has room for human error.
Step 6: Launch and post-launch support
After the development and testing is complete, you can deploy your AI into the real world. While it might seem like the end of a story, it’s not. After the deployment, it’s important to monitor how AI performs and implement changes or bug fixes if needed. Additionally, it will help you see the overall results of AI implementation and determine areas for improvement.
Final words
AI brings transformation and efficiency to every industry it touches. However, before implementing artificial intelligence, evaluate your business’ readiness. AI implementation is no easy task, and it requires a lot of work and proper data. Consider whether you have the tools and resources before opting for AI.
How Altamira can help
If you want to add AI to your business, but don’t know where to start, our approach will reduce your stress.
After seeing countless organisations struggle with AI implementation, we developed a workshop that strips away the complexity. No jargon. No hype. Just clear paths to value.
Our approach focuses on three key questions:
1. Where are your current business pain points?
2. Which processes could benefit from AI enhancement?
3. What's your readiness for implementation?Natalie Semak, Altamira’s Chief Delivery Officer
Our zero-headaches approach ensures your AI integration goes smoothly. Modernise your business with bespoke AI-powered software and reap its benefits.
Contact us and get ready for AI to improve your business.
FAQ
The best way to implement AI is to start with a clear business objective. AI should solve a specific problem and not be adopted for its own sake. Businesses should evaluate their data readiness, choose the right AI tools, run pilot tests, and continuously monitor performance to avoid AI implementation challenges.
AI implementation typically involves several key stages: defining business goals, assessing data availability, selecting AI technologies, developing and training models, testing in a controlled environment, and finally, deploying and monitoring performance. Each stage requires careful planning to avoid costly mistakes.
AI implementation varies in complexity. Some AI-powered tools are easy to integrate, while custom AI models require significant expertise and data preparation. Businesses must consider whether they have the right resources and whether off-the-shelf AI solutions or custom development is the better route.
A successful AI strategy starts with a clear vision. Identify which business areas will benefit from AI, ensure data readiness, select the right AI framework, and set measurable goals. It’s also crucial to involve key stakeholders, run pilot projects, and refine AI systems based on real-world performance before scaling up.






