Table of Contents
The true potential of data can reinvent the business processes within organizations and create an extra competitive edge. Unfortunately, a significant percentage of small- and middle-sized businesses lack an understanding of the importance of data, and those who comprehend, struggle to implement efficient practices to access data value.
Intentionally or not, every modern business generates vast amounts of data. The question is how the companies use it.
So, how can businesses approach the challenges related to data? The answer would be an implementation of proper data management and data strategy framework, and we would explain how it works.
Why Should You Care about Data Management?
Data management is a process of collecting, storing, maintaining, and protecting all the data a company gathers. As we’ve mentioned, every organization possesses such a powerful asset as data, but to really use it, businesses need to keep it accessible, reliable, and scalable. And data management strategy is key to achieving these results.
Data management includes the next aspects:
- data governance;
- data architecture;
- data storage;
- data quality management;
- master data management;
- data visualization;
- data engineering;
- database management;
- data warehousing and business intelligence management;
- data federation.
Proper data management allows companies to leverage data for business value generation. It also allows enabling of more profound technologies like artificial intelligence, machine learning, and advanced analytics, which, in turn, can amplify the value and advantages at times.
In general, the implementation of data management brings three main improvements to businesses: reduced expenses, enhanced client services, and new revenue streams. These three points usually become the main drivers for businesses of any industry and size to consider implementing data management in its different forms.
So, to guide you through the subtleties of the data management implementation, we asked Tomas Masek, the COO of Altamira, to share the most critical data management processes and practices every company should adopt.
Data Solutions Advice
Get a complimentary consultation about Data Services for your business
Practice #1: Defined Business Goal
Any initiative should be driven by the goal. So, before you make any decision regarding the implementation of any type of data management and strategy approach, you should understand what result you want to achieve. This comprehension will define the type structure of data you need to gather and processes, which, in turn, will determine your data strategy.
So, when determining your goals, you might lean on the following questions:
- what do you expect from your data? Should they help you to take decisions? Do you want to sell them?
- what issues do you want to resolve / what opportunity do you want to develop?
- what types of data do you need for what purposes?
- do you need access to your data in the real-time or is it okay to have them static?
- what is the role of data in achieving your final business goal?
Practice #2: Data Accuracy and Quality
Data quality is the measure of how well data is prepared to be used for analysis and further decision-making. It usually consists of six dimensions; even if only one is compromised, you risk encountering issues that will jeopardize the value you might have received.
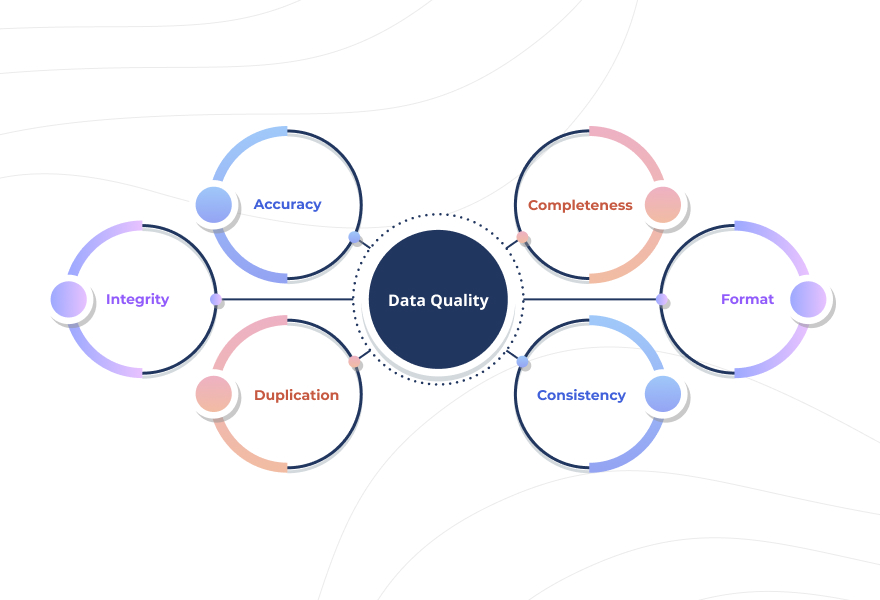
Inaccurate data will provide you with unreliable analysis results, will increase costs on data management and maintenance, devaluate data visualization, and might also generate additional operational expenses.
For example, inaccurate data or wrongly structured data in your CRM will take time to correct from your sales team, while they could dedicate these efforts to building customer relationships. Or, the mismatch in financial data due to poor data management might lead to making wrong decisions, and this, in turn, might bring financial losses and reputation damage.
So, how to avoid such situations? Here are a few tips.
- Rely on a single data source: often, data is gathered from multiple sources, and organizations unnecessarily duplicate data, creating additional workload and data discrepancies.
- Maintain data properly: all the data should be maintained carefully, you should ensure that the data is of proper quality before making any decisions based on it;
- Maintain discipline: always ensure that the data is gathered and inputted correctly;
- Automate wherever possible: avoiding human failures by automation of data flows leads not only to better data quality but also to reduced overheads.
Practice #3: Data Ownership
Data ownership is often overlooked as other aspects of data management become a priority. However, having data owners who are accountable for specific data sets helps companies to keep data in constant order, control data quality, address issues without delay, and ensure compliance. Data Ownership doesn’t mean the actual possession of the data by a certain person, but rather assigning a person to be responsible for certain data or data flows within the organization.
So, when you implement a data management approach, make sure that every piece of the enterprise data has a data owner who would be liable to take care of it. It is also important to avoid data being assigned to multiple data owners (e.g, several departments).
So, when you implement a data management system, make sure that every piece of the enterprise data has a data owner who would be liable to take care of it. It is also important to avoid data being assigned to multiple data owners (e.g, several departments).
Practice #4: Automation
Simple rule: if it can be automated, it should be automated. Of course, the same is valid when thinking about data management and strategy approaches. Data flow automation means that data gathering, handling, and processing are done by automation tools, which might be a part of software solutions used, or developed. The main processes here include extracting, transforming, and loading the data, abbreviated as ETL.
The ground for implementing data automation is obvious: it removes the need for manual input. When you rely on employees processing the data, most probably, you will need to get ready for delays, data errors, and additional costs. Automation reduces these risks and at the same time becomes a necessity. In the era of big data, companies generate so huge volumes of data that it is impossible to rely on humans to process them.
Hence, our advice here would be to always automate your data processes as much as it is possible for your business.
Practice #5: Data Repository
The way you store your data affects how efficiently you can leverage it. If your data is scattered among data silos aka Excel spreadsheets created by different employees, you will definitely struggle to implement any pivoting changes and make data accessible and applicable to the whole enterprise.
Hence, you need to store all the data you get from different data sources in one centralized system — a data repository. This way, the data can be easily found and reviewed by anyone in the company. Also, it would be much easier to conduct further manipulations with your data, like running a business analytics tool.
There are a few types of data repositories that businesses usually use: data warehouse (for structured data), data lake (for structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data), and data lakehouse (for structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data; combines the advantages of both data warehouses and lakes).
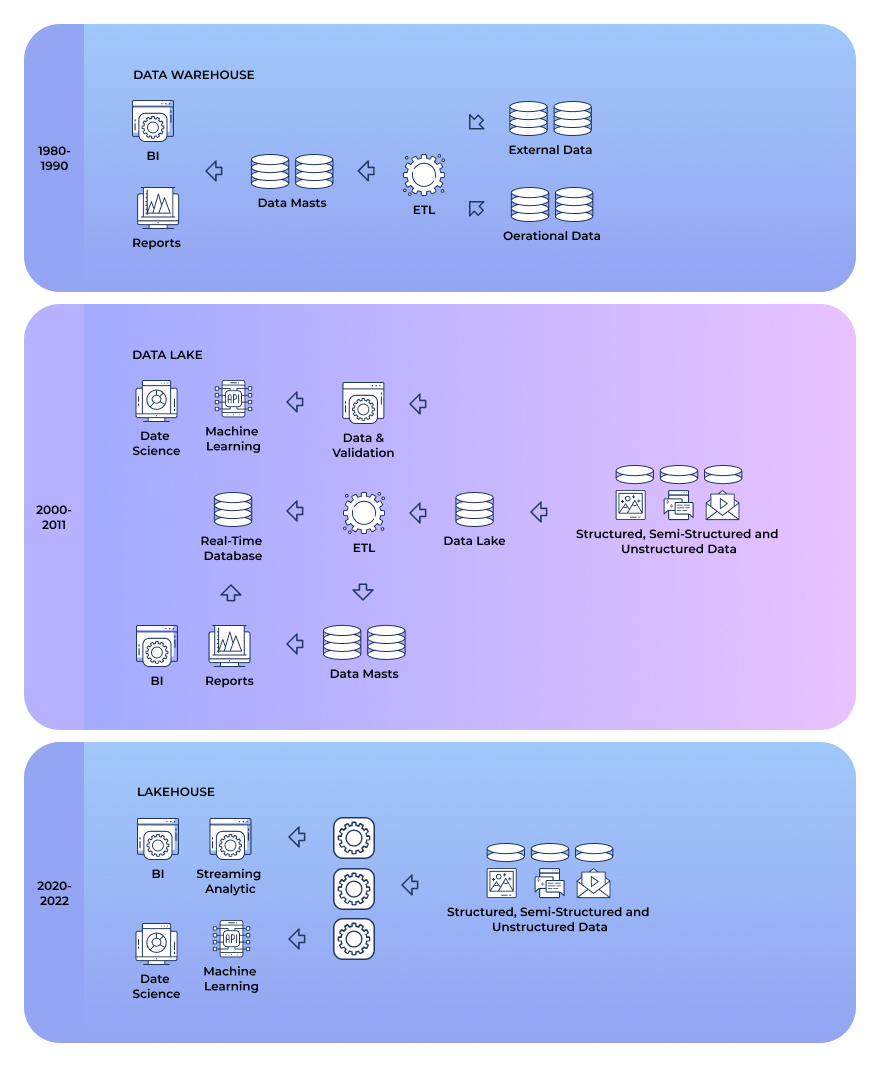
Practice #6: Data Access and Visualization
This is a logical continuation of the previous paragraph. Data will bring the most value when it is easily accessed. Ideally, your employees should not wait long to get data; it should be accessible in real-time.
The same goes for visualization. Visualizing the data in charts, maps, graphs, infographics, dashboards, etc. makes more sense for people using it. It helps to see patterns and dependencies, especially if we are talking about big data volumes that can hardly be comprehended otherwise.
There are a lot of visualization tools available on the market (Tableau, PowerBI, etc.), which are capable of delivering great added value of having data visualized quickly and easily
Practice #7: Data Security
As we have mentioned, data is an asset so that it can be stolen, compromised, or tempered. You definitely don’t need to hear about data leaks and their impact on business — such cases quickly become public knowledge and big brand damage. So, data protection and security should be a priority for any company, considering that any breach of personal data might lead to broken compliance, and leaked trade secret is a huge danger to the business’s competitive edge.
So, what action should the company take to prioritize data protection?
- Sensitive data should be encrypted.
- Data access should be based on a clear user permission model.
- Every access should be monitored to detect any suspicious activity immediately.
- Organizations should not allow usage of public repositories to store sensitive data (Github, Gitlab, Public data storages, etc.)
Practice #8: Data Backups and Versioning
Data backup is one of the most critical aspects of your data integrity. Businesses can’t risk losing crucial databases or line-of-business applications, and there are a lot of possible scenarios which can lead to the loss or corruption of the data:
- software or hardware failure
- malware or hacker attack
- user error, device theft, or loss
- natural disaster or any other kind of emergency you might not expect.
The next level of data backups companies might dismiss but should really implement is data versioning. Having the previous versions of data saved and safely stored will help recover necessary information at any point in time and contribute to measuring performance over the years and going through audits without stressing about missed reports.
Still, an important question is: how often should you back up the data? Ideally, every 24 hours. However, it might not be possible for some enterprises, and they run their backups once a week, mainly during work-off hours (night or weekends).
The creation of data backups can be automated as well: there are dozens of tools that can enhance this process and with the rise of cloud storage and backup services, enterprises don’t need to invest in hefty and expensive hardware to keep their backups.
Altamira as Your Reliable Data Management Vendor
Effective data management is essential, but enterprises of different sizes might be lacking the expertise and resources to implement it on their own. A simple and thoughtful solution would be to apply to the team of experienced data management specialists who will be able to build a strong data infrastructure and set up necessary data management practices.
Altamira’s team offers a wide data solution landscape for startups, medium-sized businesses and enterprises. We can create the most suitable data framework tailored specifically to your company’s needs, and implement all the must-have data management practices we mentioned.
Success Story : Data Management Service for Statrix - pharma data analytics platform
The data analysis platform gathers data about drug prescriptions from different sources used by pharmaceutical companies in pharmaeconomical studies to support their drug registration process and price negotiations with the regulator.
Our solutions:
- Designing a complex data warehouse model (process, data flow, data model) able to handle large amounts of data.
- ETL: extracting, transforming, and loading data from several sources into the data warehouse.
- Development of a full-scaled BI software infrastructure from scratch on top of the mentioned.
In Conclusion
Data management opens new perspectives and opportunities for businesses in any industry, which is especially valuable during the recession. Data is already an asset your company possesses, so why not handle it more efficiently to monetize it and leverage additional business value?
FAQ
Data management is the process of gathering, storing, using, and archiving data. Data management covers all phases of the data lifecycle and implements necessary policies and practices to organize it.
Data management helps companies to organize their data and keep it that way, so it would be possible to extract business value from it and implement it to discover new business opportunities and revenue streams or optimize operational processes.



