Table of Contents
About some time ago we have covered the many faults and problematic disruptions delivered by the Big Tech corporations. Just the same there’s a worldwide criticism directed at the variety of modern innovations, many of which can be of great benefit for human society. You can add to it the rising combination of high tech upgrades with medical research aimed to enhance all life aspects for us mortals. We may even live forever by uploading our consciousness into cloud to exist virtually in the digital world. Who knows?
As of yet, facial recognition is one of the most interesting and attractive technologies adopted widely across all spheres and niches of software development industry. You can face unlock your iPhone now and in about a year or two your smart home assistant will be able to know that it’s you not just by your voice.
We will discuss the technology and business ideas behind its widespread adoption, considering the impact it can potentially have on democracy and liberal values, and the many benefits it can deliver to us, users.
What is Facial Recognition?
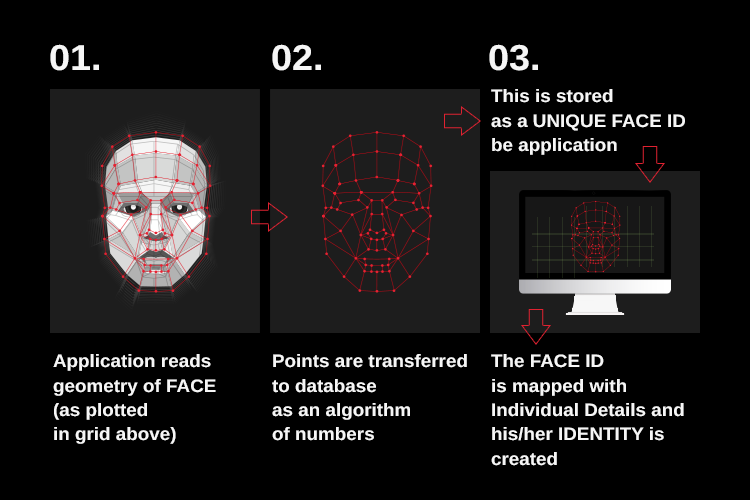
FR detects the presence of a user if there is previous data that allows comparison. For example, you may let a program make a photo of you. You can change the time and place to make another photo and the program will compare two pictures and claim that it is you, analyzing two photos. It is possible to do that even without making the first photo specifically, it can be any photo made earlier.
The underlying engineering of this program consists of what the neural network does with two photos, processing them. It works the same with live footage. A program uses images to memorize and then compare the information to issue a verdict whether the two photos indicate a single identity.
Artificial Neural Networks are algorithmswidely used in image recognition. The program outperforms itself each time and becomes more skilled over time if provided with the source of data to use.
Take two pictures, one of a cat and one of a horse, and provide the system with more pictures. After a 100 or a 1000 comparisons the machine learns what is a HORSE and what is NOT HORSE and what is a CAT and what is NOT CAT. Another part of the equation is condition that NOT A HORSE = CAT and NOT A CAT = HORSE. With the following inputs the program is going to make a difference between cats and horses.
This easy process has many complex variations and much more sophisticated algorithms exist that calculate and simultaneously process the amount of information a human brain simply cannot process at once. Not a cat is not necessarily a horse in real life, right? It can be a dog. But that requires additional programming.
How Does It Work?
You can give your photo to the program, it will look in its database for the comparison to first indicate who you are by comparing you present to the photo that is used to identify you. It is kind of like when a police officer checks your ID and compares the photo with your live face as of the moment.
Given the photo of you and seeing what you look like in the moment results in the officer identifying you as the person it is said you are on the document, for example, John Smith. Given the photo of John Smith that is labeled John Smith, the system connected to a camera will know John Smith when seeing one.
The same as cats have tails we have a myriad of different features on our faces. For a program this is information and nothing more. It can learn that something with a tail is a cat and that a cat is an animal and that many animals have tails, though not all of them are cats. In the same manner a neural network in image recognition technologies can tell when it sees a Rembrandt painting or a Van Gogh painting, a Pepsi or a Coke, a car or a truck. etc.
The system doesn’t understand or make a rational decision but simply picks similarities in the data it is provided with. Processing 2 inputs, 4 inputs or 4 000 000 MB of inputs is just a power/speed problem but it is very possible. This is just the beginning of what an algorithm can have knowledge of and it can learn further on its own. What can be done should be done, right? So let it learn. The bigger a data set is, the more precise are the outcomes.
What’s the Media Coverage Like?
The most widespread adoption of the face recognition technology is currently occurring in China where users can purchase groceries and pay by simply scanning their faces. That complies with China being a surveillance state that disregards individual rights and privacy freedoms of its citizens. That is a present reality. But that is not why facial recognition has become so popular recently.
Media provides extensive coverage of the government attempts to deploy facial recognition technology in public surveillance. The public in California, US and Australia actively oppose the use of technology by government since it became known that algorithms are not perfect and may produce errors, especially in recognizing the representatives of ethnic minorities, people of Hispanic origin and Afro-Americans.
Many people are afraid that with facial recognition technology the invasion of privacy is inevitable and that government can easily put it to bad use. There is even a greater debate over its adoption in military while for governments it first and foremost means a greater order and more optimized storage of citizen profile data for more secured and regulated state-citizen communication and affairs. This can be considered a continuation of a biopasport. State has your fingertips, your name, your address, your telephone number, your marital status and everything else. It wants your face too.
FAQ
Conclusion
Facial recognition is a technology that has already experienced a wide adoption. You can unlock your phone by scanning your face or pay via the terminal installed where the cashier is. Given the rate of surveillance today, facial recognition in future will be able to know everybody on the street, matching the photo with the identical one in its ID storage.
California citizens consider that this technology in the hands if government is a recipe for disaster because of the horrors that its corrupt use can bring. In China, though, this is already a reality while UK and Australia come closer and closer to the same decision of the use of facial recognition big time. Whatever the future brings, one thing is sure, though, and that is the fact that facial recognition can be useful.