Table of Contents
Building a minimum viable product (MVP) is a widely known practice that helped many entrepreneurs save a lot of money and time in the early stages of startup development. Many world-known unicorns have started with MVP, for instance, Uber, Dropbox, Figma, and Slack. But what works for one doesn’t necessarily work for the others. And definitely without a clear understanding of MVP purpose, you can lose more than win.
What is a Minimum Viable Product (MVP)? A brief overview
Let’s start by defining the term MVP. Minimum viable product (MVP) is a term coined by Frank Robinson and popularised by Eric Reis, as a part of the Lean Sales methodology. It means a product with a minimum feature set used to collect the maximum amount of validated learning about customers with the least effort. Its main purpose is to gather insights, test your concept, and connect with the company’s target market by spending less time and money.
Limiting the product’s functionality and constraining the number of features to a few that satisfy the audience’s basic needs can reduce costs. Later, you can improve your product to retain early adopters.
In reality, the concept of MVP is often confused with the term technology prototype and is not related to the development process. MVP (minimum viable product) is a way to test business hypotheses and validate the technology prototype’s sale. Such testing with the audience allows for discovering the further iterations needed to enhance the value development.
Cases when MVP is needed
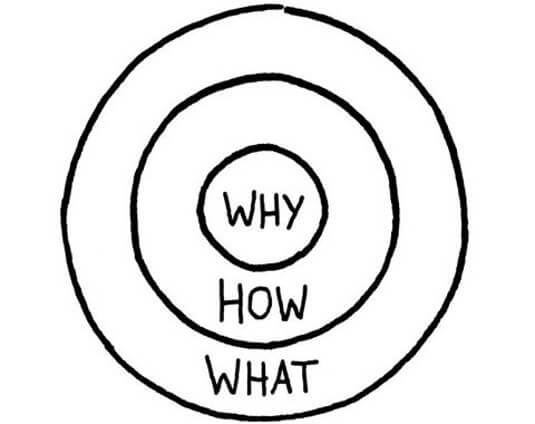
Remember Simon Sinek’s Golden Circle framework? “People don’t buy what you do, they buy why you do it”
Why, How, and What – three questions your MVP should be built around. If your product is the answer to those questions, then the minimum viable product should test your answers.
If you have an idea but don’t know whether customers will appreciate it, ask them and do marketing research! That way, you’ll get the answers to the “why” question.
Next, start the start development of a minimum viable product in order to get an answer to the “How question”. You need to test whether it is possible and profitable to build and maintain such a product. It may be too pricey or too complex.
Congratulations! After your MVP is ready, you can pitch it to VC funds, private investors, and users.
Software minimum viable product has some additional advantages. It is much leaner and more flexible, so it takes less time and resources in order to adjust the product according to data gathered during research. Meaning you will spend less money in order to tweak and reshape your software MVP or mobile app prototype.
Maybe this Is not the MVP you are looking for?
With the boom of startups, the minimum viable product gained a sacred must-have image. Customers accept simple products. Nevertheless, one should understand that MVP is not a magic pill that solves all troubles. There is no MVP business! Here’s what David Schwartz, Senior Director of Product Management of Wix (One of the biggest website development platforms to date) said about MVP:
“People are mistaken about what MVP is. MVP is not a product you’re taking out there. The product you’re taking out there is called the First Phase. MVP is an experiment!”
We had several cases when clients insisted on developing an MVP when all they needed was an experiment or deep market research. Moreover, there are many reasons why you may dump an MVP in your business and make a full-bodied product from the start.
- MVP is not a profitable product you can sell.
- You can’t test all your assumptions with MVP.
- The minimum viable product is not free. It does need time and money to develop as well as the product.
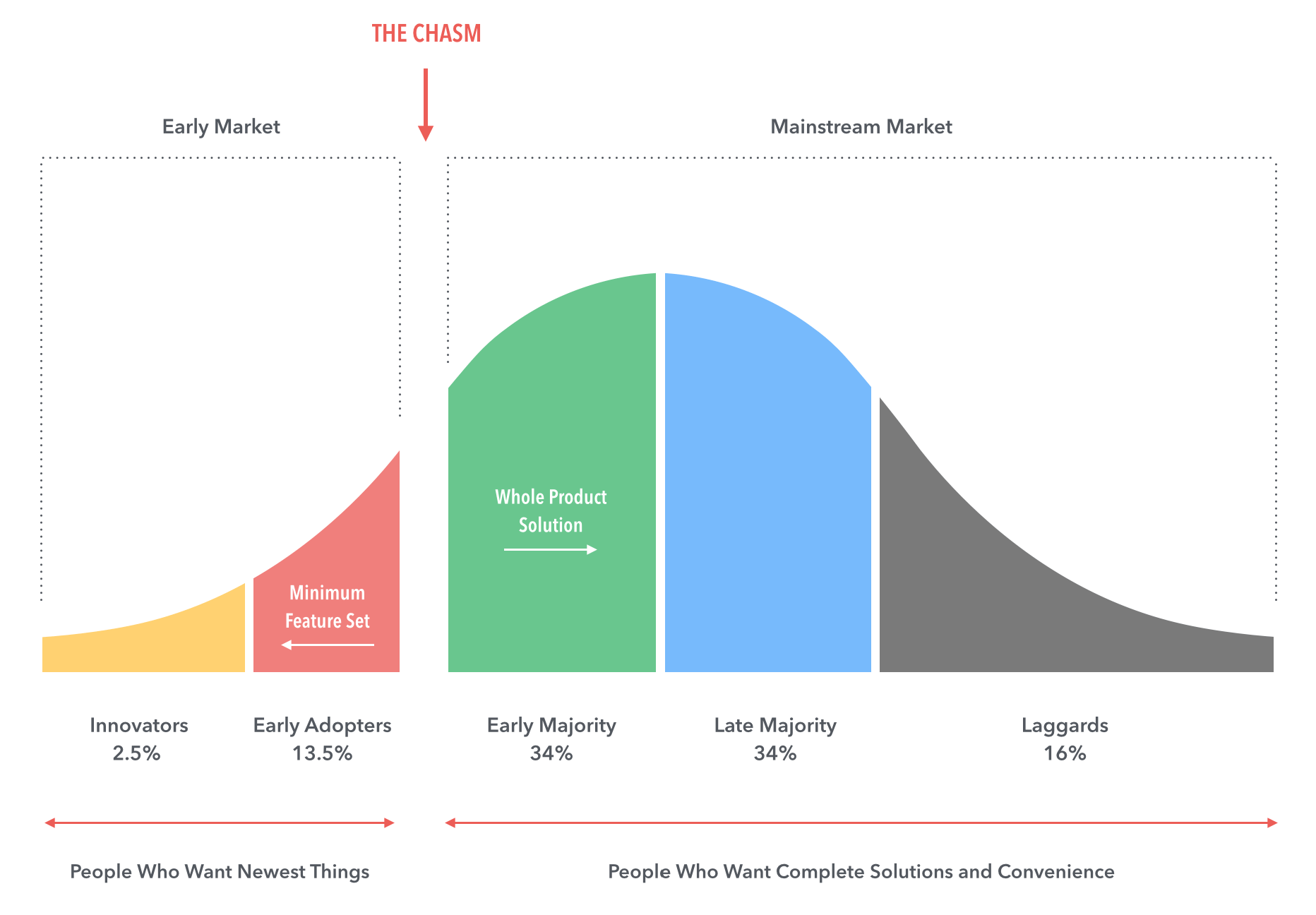
MVP won’t help you to cross the Chasm!
A minimum viable product can usually survive for some time. It is acceptable and functional, so innovators and even users can be happy with it.
But there is time to get to the mass market in order to earn real revenues. To get there, you’ll need to cross that Chasm. This is where most projects from Kickstarter end up. They get funded by innovators, praised by users, and then die without winning the hearts and minds of the majority.
Here’s a list of successful minimum viable product examples and then unsuccessful products that seemed to conquer the market but failed to gain customers’ trust:
- BETAMAX lost to VHS.
- Microsoft Zune lost to iPod.
- Myspace lost to Facebook.
- HP’s Touchpad lost to iPad.
- Pebble was eventually purchased by Fitbit.
That’s what Chasm does to great, innovative products.
One reason Chasm happens is that entrepreneurs can’t step back and reshape their MVPs into a mass-market product. Indeed, doing so may be really challenging, even after struggling so much to create an MVP.
First of all, you should preserve the core innovation that was so popular among early adopters. Second, it may be controversial, you should mask that innovation into more trivial shape. At this point, you may be criticised by innovators and those customers you’ve already acquired, but this is how you find a way to the heart of a grand audience.
Definitely, from such a point of view, developing a full-fledged minimum viable product can be a huge waste of time and money. And the profitability of investing in MVP is reduced proportionally to the size of the innovator’s community you are targeting with the product.
Don’t go with an MVP if the innovators and early adopters of your targeted audience won’t give your product enough attention and investments to develop a complete product.
Alternatives to MVP
Riskiest assumption test
This approach addresses several uncertainties related to MVP. For example, how “minimal” should your minimal viable product be? What hypothesis should it test? Should it explore only one assumption or all of them?
The risk assumption test has a single answer to all these questions: Test the biggest uncertainty you have. Meaning you don’t want to build more than needed to test the largest unknown.
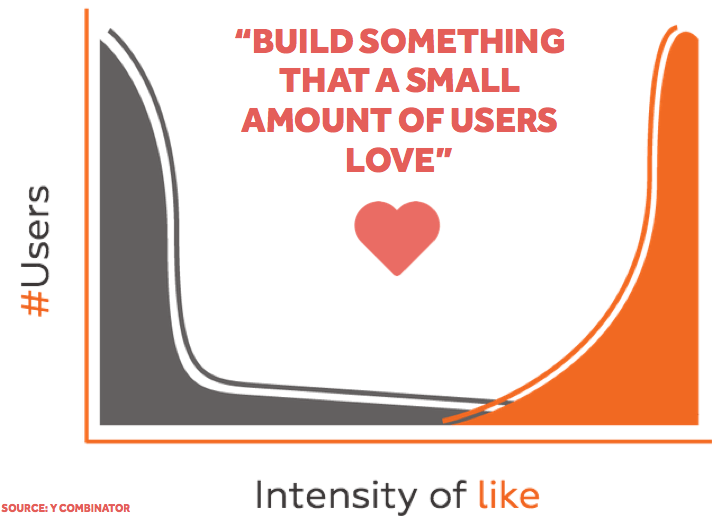
Minimum loveable product
It is a term coined by Brian de Haaff, founder of the road map software Aha! MLP suggests entrepreneurs develop a product that aims to satisfy the customer satisfaction of a small targeted audience. That way, you will save money on added features that target the wider user group.
In addition, advocates of MLP site that minimal viable products are usually built to prove the entrepreneur’s business concept (processes, logistics, product structure) rather than audience interest.
The difference between MVP and MLP
| MLP principles | MVP principles |
| Goal is to disrupt | Goal is to increment |
| Problem can be understood | Problem cannot be understood |
| Market can be analyzed | Market cannot be analyzed |
| Customers know what they want | Customers do not know what they want |
| Many product alternatives exist | Few product alternatives exist |
| Make architecture decisions because technology is sufficiently stable | Avoid architecture decisions because technology is unpredictable |
| Dedicated effort to the opportunity | Lean effort because success is unlikely |
| Focus | Pivot |
| Customers love your product | Customers tolerate your product |
Kano model
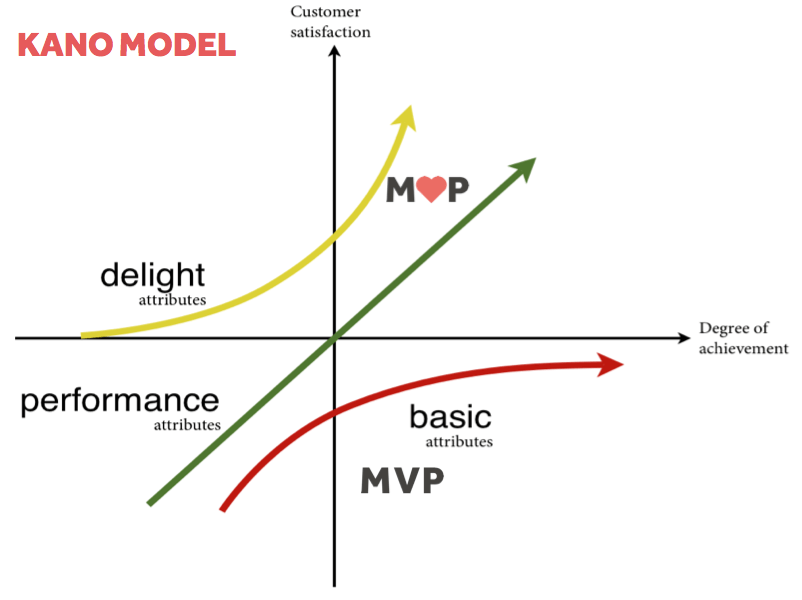
We suggest you get familiar with the Kano Model in order to avoid such mistakes.
Kano Model examines each product from a customer satisfaction perspective. It classifies customer preferences into five categories and suggests keeping in mind only those product features that maximise customer satisfaction.
- Must-be quality. A functionality that is not new and taken for granted.
- One-dimensional quality. The presence of these features results in the rise of customer satisfaction, the absence of those features decreases it.
- Attractive quality. The most innovative set of features creates a WOW effect, but it risks being misunderstood by users.
- Indifferent quality. Features that do not affect customer satisfaction. E.g. Programming Language or Framework used to develop an app.
- Reverse Quality. Over-exaggerating these qualities results in the loss of some customers. E.g. Oversimplification of the product may divert tech geeks. The complication may divert users with low-tech savviness.
Focus on the first two qualities if you’re building MVP for a unique product. Spend more effort on the second and third qualities if you’re entering a highly competitive market.
Minimum marketable product
It is a term presented by Mark Dene and Jane Cleland-Huang in their 2003 book Software by Numbers. MMP means a product comprising a minimal set of features needed to test a feasible marketing model.
This term actually combines the MVP and MLP. You have already understood your target audience, gathered the feedback, and fully understood the problem your product is going to fix.
The new MVP alternatives
The lean startup methodology’s approach is based mainly on end-user feedback: a well-known build-measure-learn feedback loop. In the evolving digital environment, newly emerged MVP alternative methods validate the business idea or startup model.
Minimal catchy offer
It can be presented in one sentence. The key characteristics are clarity, effectiveness, and speed. If you are still considering whether it is worth investing in the MVP concept, it could be a good alternative. It can be a short slogan or a condensed but efficient video, allowing the target user to understand the value proposition your business idea offers.
Example
MasterCard’s slogan, “There are some things money can’t buy. For everything else, there’s MasterCard.” was part of an ad campaign presented by a TV commercial. In the commercial, a dad takes his son to baseball games, pays for a hot dog and drink, and spends time together, which is priceless.
Black hole strategy
The black hole strategy is focused on finding alternatives or hidden instruments that can influence the regular behavioral patterns of target users and change the way people act in particular situations.
Example
Many software development companies offer courses to educate new developers. However, given the current situation, where everyone is trying to educate themselves, a better option would be to create a platform supporting self-education.
Lean investor
This method is part of the lean startup methodology and proposes investing in startups using incremental investment and iterative development. You can start with simple experiments, refuse and analyse failures, and expand investments in successful deals.
How Altamira can help you with MVP launch
The choice of a software development company is a crucial aspect. You need to choose a partner who has extensive experience in MVP development and can guide future development smoothly.
Our developing teams have profound experience and cross-industry expertise, allowing them to help companies build impressive MVPs. We deliver solutions for EdTech, eCommerce, pharma, FinTech, and beyond, guiding customers through the whole product development cycle.
Our successfully completed projects allow us to build efficient MVPs and help you accelerate time to market and time to revenue with ease.
By choosing us as a development partner, you get:
- Rich cross-industry expertise;
- Discovery stage to validate the initial product idea;
- Fast time to market;
- Fast time to revenue;
- Customer-centric approach;
- Agile methodology development practices;
- NDA compliance;
- Business analysis and efficient project management;
- Solid MVP that could be successfully scaled in the future;
- Assistance in software implementation and further maintenance.
At Altamira, we use a flexible approach, thus you may choose the cooperation model that suits you the most. It could be either from team extension services or outsourcing cooperation models.